The Rise and Reach of the Plant-Based Food Market
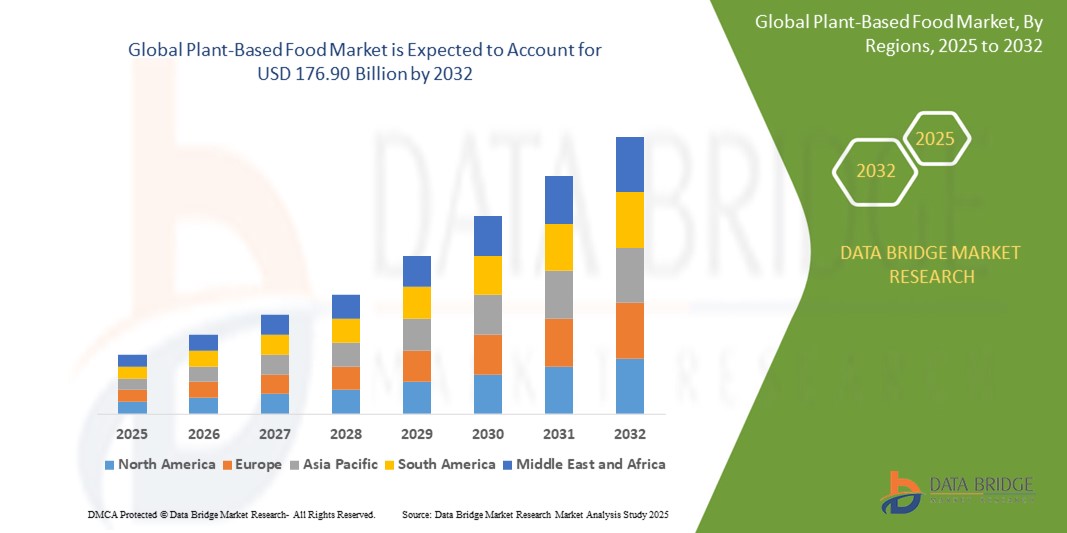
The global plant-based food market will grow from USD 28.38B in 2024 to USD 176.90B by 2032, driven by health, environmental, and ethical awareness.
Introduction
The Plant-Based Food Market has emerged as one of the most dynamic and transformative sectors in the global food industry. Driven by shifting consumer preferences, environmental concerns, and advances in food technology, plant-based alternatives are no longer niche products—they are reshaping how people eat, shop, and think about nutrition. From dairy-free milks to meatless burgers, the market is expanding rapidly across continents, demographics, and retail channels.
This surge is not just a trend but a reflection of deeper societal changes. Health-conscious consumers are seeking cleaner labels, ethical sourcing, and sustainable production. Meanwhile, food companies—both startups and legacy brands—are racing to innovate and capture market share. The Plant-Based Food Market is now a battleground of creativity, science, and strategy.
The Evolution
The journey of plant-based foods began decades ago, primarily as a lifestyle choice among vegetarians and vegans. Early products were often limited in variety and appeal, catering to a small segment of consumers. Tofu, tempeh, and soy milk were among the few available options, and they were largely confined to health food stores or specialty markets.
In the 1990s and early 2000s, awareness around animal welfare and environmental sustainability began to grow. Documentaries, advocacy campaigns, and scientific studies highlighted the impact of industrial animal agriculture on climate change, deforestation, and water usage. This catalyzed a broader interest in plant-based diets.
The real inflection point came in the 2010s, when food technology companies began developing plant-based products that mimicked the taste, texture, and appearance of animal-derived foods. Brands like Beyond Meat and Impossible Foods introduced burgers that sizzled, bled, and grilled like beef. These innovations broke the barrier of taste and brought plant-based eating into mainstream culture.
Retailers responded by expanding shelf space for plant-based products. Fast food chains added meatless options to their menus. Celebrities and athletes endorsed plant-based lifestyles. The market evolved from a niche to a movement.
Market Trends
Several key trends are shaping the Plant-Based Food Market today:
- Diversification of Product Categories: Beyond meat and dairy substitutes, the market now includes plant-based seafood, eggs, snacks, desserts, and ready-to-eat meals. This diversification is attracting a wider consumer base.
- Clean Label and Minimal Processing: Consumers are scrutinizing ingredient lists. Products with fewer additives, recognizable ingredients, and transparent sourcing are gaining traction.
- Global Expansion: While North America and Europe lead the market, Asia-Pacific and Latin America are witnessing rapid growth. Cultural adaptations and regional flavors are helping plant-based products gain acceptance in diverse markets.
- Private Label Growth: Retailers are launching their own plant-based brands, offering competitive pricing and exclusive formulations. This is intensifying competition and driving innovation.
- Functional Foods and Nutrition: Plant-based products are being fortified with vitamins, minerals, and protein to meet nutritional needs. Functional ingredients like pea protein, algae, and mushrooms are becoming popular.
- E-commerce and Direct-to-Consumer Models: Online platforms are enabling startups to reach consumers directly, bypassing traditional retail channels. Subscription boxes and digital marketing are fueling brand awareness.
Read More: https://www.databridgemarketresearch.com/reports/global-plant-based-food-market****
Challenges
Despite its growth, the Plant-Based Food Market faces several challenges:
- Taste and Texture Limitations: While progress has been made, replicating the sensory experience of animal-based foods remains a hurdle for many products.
- Price Parity: Plant-based alternatives often cost more than their conventional counterparts. Achieving price competitiveness is crucial for mass adoption.
- Supply Chain Complexity: Sourcing high-quality plant ingredients sustainably and consistently is a logistical challenge, especially as demand scales.
- Consumer Skepticism: Some consumers perceive plant-based products as overly processed or lacking in nutritional value. Education and transparency are needed to address these concerns.
- Regulatory and Labeling Issues: Definitions of terms like “milk” and “meat” are being contested in courts and legislatures. Regulatory clarity is essential for market stability.
- Cultural Resistance: In regions where meat consumption is deeply embedded in tradition, plant-based alternatives face resistance. Localization and cultural sensitivity are key.
Market Scope
The scope of the Plant-Based Food Market is vast and expanding. According to industry analysts, the global market is projected to reach hundreds of billions of dollars within the next decade. Growth is being fueled by multiple sectors:
- Retail: Supermarkets and grocery stores are dedicating entire aisles to plant-based products. Shelf placement, packaging, and promotions are becoming more sophisticated.
- Foodservice: Restaurants, cafes, and fast food chains are incorporating plant-based options into their menus. Partnerships with plant-based brands are common.
- Institutional Catering: Schools, hospitals, and corporate cafeterias are adopting plant-based menus to meet health and sustainability goals.
- Hospitality and Travel: Airlines, hotels, and resorts are offering plant-based meals to cater to diverse dietary preferences.
- Export and Trade: Countries are exporting plant-based products to meet global demand. Trade agreements and logistics networks are being optimized.
- Innovation and R&D: Investment in food technology is accelerating. Startups and research institutions are exploring novel ingredients, fermentation techniques, and cellular agriculture.
Factors Driving Growth
Several factors are propelling the growth of the Plant-Based Food Market:
- Health Awareness: Rising concerns about obesity, heart disease, and diabetes are prompting consumers to seek healthier alternatives. Plant-based diets are associated with lower risks of chronic illness.
- Environmental Impact: Consumers are increasingly aware of the carbon footprint of animal agriculture. Plant-based foods offer a more sustainable option.
- Ethical Considerations: Animal welfare concerns are influencing purchasing decisions. Consumers are choosing products that align with their values.
- Technological Advancements: Innovations in food science are enabling the creation of products that closely mimic animal-based foods. This is reducing barriers to adoption.
- Celebrity and Influencer Endorsements: Public figures are promoting plant-based lifestyles, increasing visibility and desirability.
- Government and Institutional Support: Policies promoting sustainability, health, and food security are encouraging the development of plant-based alternatives.
- Cultural Shifts: Younger generations are more open to experimenting with diets and are driving demand for plant-based options.
- Investment and Funding: Venture capital and corporate investment are fueling growth. Mergers, acquisitions, and partnerships are consolidating the market.
Browse More Reports:
Global Tea Pods and Capsules Market North America Silicon on Insulator Market Global Cannabidiol (CBD) Skin Care Market Global Biodegradable Film Market Middle East and Africa Coated Paper Market North America Molecular Diagnostics Services Market North America Glucose Monitoring Devices Market
Conclusion
The Plant-Based Food Market is not just a passing trend—it is a fundamental shift in how food is produced, consumed, and perceived. As technology advances and consumer awareness deepens, the market will continue to evolve, diversify, and expand. While challenges remain, the momentum is undeniable. Businesses, policymakers, and consumers all have a role to play in shaping the future of food. The plant-based revolution is here, and its impact will be felt across industries, cultures, and generations.